Code
Sys.setenv(RETICULATE_PYTHON = "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11/bin/python3.11")
library(reticulate)
use_python("/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11/bin/python3.11")Tony Duan
siuba (小巴) is a port of dplyr and other R libraries with seamless support for pandas and SQL
 Using python 3.11
Using python 3.11
keep data in left which not in right ::: {.cell}
:::
keep data in right which not in left ::: {.cell}
:::
Below 3 method will give same result
other way: ::: {.cell}
::: other way: ::: {.cell}
:::
Use .str.replace(…, regex=True) with regular expressions to replace patterns in strings.
For example, the code below uses “p.”, where . is called a wildcard–which matches any character.
Use str.extract() with a regular expression to pull out a matching piece of text.
For example the regular expression “^(.*) ” contains the following pieces:
a matches the literal letter “a”
.* has a . which matches anything, and * which modifies it to apply 0 or more times.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from siuba.sql import LazyTbl
from siuba import _, group_by, summarize, show_query, collect
from siuba.data import mtcars
# copy in to sqlite, using the pandas .to_sql() method
engine = create_engine("sqlite:///:memory:")
mtcars.to_sql("mtcars", engine, if_exists = "replace")because lazy expressions,the collect function is actually running the sql. ::: {.cell}
:::
https://siuba.org/
---
title: "Data manipulation with siuba(not working with current pandas version)"
author: "Tony Duan"
execute:
warning: false
error: false
eval: false
format:
html:
toc: true
toc-location: right
code-fold: show
code-tools: true
number-sections: true
code-block-bg: true
code-block-border-left: "#31BAE9"
---
{width="434"}
siuba (小巴) is a port of dplyr and other R libraries with seamless support for pandas and SQL
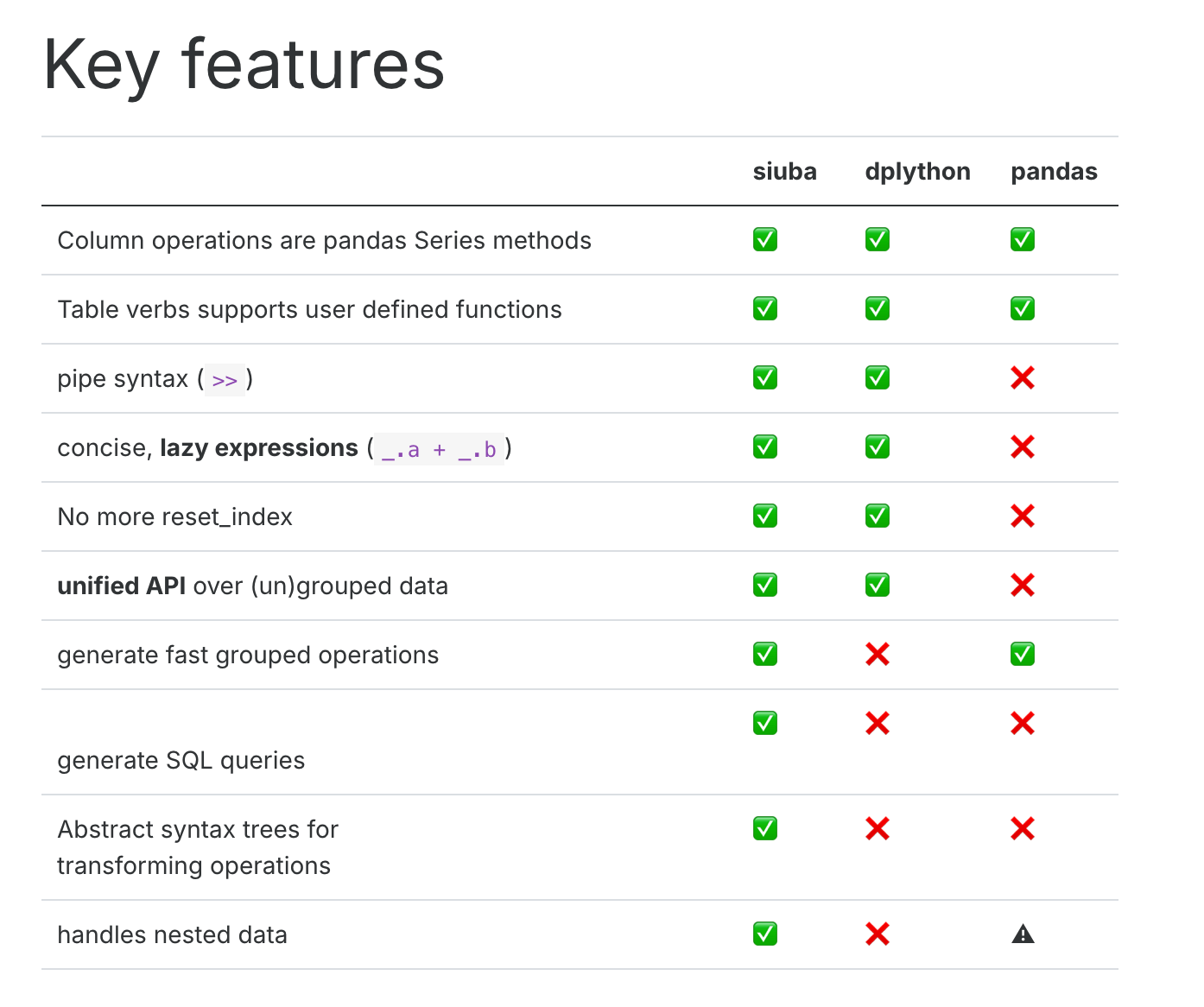
## Comparison with different python dataframe package
{width="656"}
Using python 3.11
```{r}
Sys.setenv(RETICULATE_PYTHON = "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11/bin/python3.11")
library(reticulate)
use_python("/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11/bin/python3.11")
```
## load package
```{python}
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import seaborn as sns
from siuba.siu import call
from siuba import _, mutate, filter, group_by, summarize,show_query
from siuba import *
from siuba.data import mtcars,penguins
```
```{python}
small_mtcars = mtcars >> select(_.cyl, _.mpg, _.hp)>> head(5)
```
## select column
### get column names
```{python}
list(small_mtcars)
```
### select columns by name
```{python}
small_mtcars >> select(_.cyl, _.mpg)
```
### select columns by name match with 'p'
```{python}
small_mtcars >> select(_.contains("p"))
```
### select columns by index
#### select first and 3rd columns
```{python}
small_mtcars >> select(0,2)
```
#### select first to 3rd columns
```{python}
small_mtcars >> select(_[0:3])
```
## drop column
```{python}
small_mtcars >> select(~_.cyl)
```
## Renaming column
```{python}
small_mtcars >> rename(new_name_mpg = _.mpg)
```
## Create column
### Mutate
```{python}
mtcars.head()>> mutate(gear2 = _.gear+1
,gear3=if_else(_.gear > 3, "long", "short")
,qsec2=case_when({
_.qsec <= 17: "short",
_.qsec <= 18: "Medium",
True: "long"
})
)
```
### Transmute,create column and only keep this column
```{python}
mtcars.head()>> transmute(gear2 = _.gear+1)
```
## Filter rows
```{python}
mtcars>> filter(_.gear ==4)
```
### Filters with AND conditions
```{python}
mtcars >> filter((_.cyl >4) & (_.gear == 5))
```
### Filters with OR conditions
```{python}
mtcars >> filter((_.cyl == 6) | (_.gear == 5))
```
### filter row with index
#### first 3
```{python}
small_mtcars>>head(3)
```
#### last 3
```{python}
# not in siuba, in pandas
small_mtcars.tail(3)
```
#### 5th rows
```{python}
# not in siuba, in pandas
mtcars.iloc[[4]]
```
#### 1 and 5th rows
```{python}
# not in siuba, in pandas
mtcars.iloc[[0,4]]
```
#### 1 to 5th rows
```{python}
# not in siuba, in pandas
mtcars.iloc[0:4]
```
#### get ramdon 5 rows
```{python}
mtcars.sample(5, random_state=42)
```
## Append
### append by row
```{python}
# not available in siuba yet
#from siuba import bind_rows
```
```{python}
# using pandas
# get 1 to 4 rows
data1=mtcars.iloc[0:4]
# get 9 rows
data2=mtcars.iloc[10:11]
data3=pd.concat([data1, data2], ignore_index = True,axis=0)
data3
```
### append by column
```{python}
# not available in siuba yet
#from siuba import bind_columns
```
```{python}
# using pandas
data1=small_mtcars>>select(_.mpg)
data2=small_mtcars>>select(_.cyl)
data3=pd.concat([data1, data2],axis=1)
data3
```
### Dropping NA values
### keep NA values
## group by
### average,min,max,sum
```{python}
tbl_query = (mtcars
>> group_by(_.cyl)
>> summarize(avg_hp = _.hp.mean()
,min_hp=_.hp.min()
,max_hp=_.hp.max()
,totol_disp=_.disp.sum()
)
)
tbl_query
```
### count record and count distinct record
```{python}
mtcars >> group_by(_.cyl) >> summarize(n = _.shape[0])
```
```{python}
mtcars >> group_by(_.cyl) >> summarize(n = _.hp.nunique())
```
## order rows
```{python}
small_mtcars >> arrange(_.hp)
```
### Sort in descending order
```{python}
small_mtcars >> arrange(-_.hp)
```
### Arrange by multiple variables
```{python}
small_mtcars >> arrange(_.cyl, -_.mpg)
```
## join
```{python}
lhs = pd.DataFrame({'id': [1,2,3], 'val': ['lhs.1', 'lhs.2', 'lhs.3']})
rhs = pd.DataFrame({'id': [1,2,4], 'val': ['rhs.1', 'rhs.2', 'rhs.3']})
```
```{python}
lhs
```
```{python}
rhs
```
### inner_join
```{python}
result=lhs >> inner_join(_, rhs, on="id")
result
```
### full join
```{python}
result=rhs >> full_join(_, lhs, on="id")
result
```
### left join
```{python}
result=lhs >> left_join(_, rhs, on="id")
result
```
### anti join
keep data in left which not in right
```{python}
result=lhs >> anti_join(_, rhs, on="id")
result
```
keep data in right which not in left
```{python}
result=rhs >> anti_join(_, lhs, on="id")
result
```
## Reshape tables
```{python}
costs = pd.DataFrame({
'id': [1,2],
'price_x': [.1, .2],
'price_y': [.4, .5],
'price_z': [.7, .8]
})
costs
```
### Gather data long(wide to long)
Below 3 method will give same result
```{python}
# selecting each variable manually
costs >> gather('measure', 'value', _.price_x, _.price_y, _.price_z)
```
other way:
```{python}
# selecting variables using a slice
costs >> gather('measure', 'value', _["price_x":"price_z"])
```
other way:
```{python}
# selecting by excluding id
costs >> gather('measure', 'value', -_.id)
```
### Spread data wide(long to wide)
```{python}
costs_long= costs>> gather('measure', 'value', -_.id)
costs_long
```
```{python}
costs_long>> spread('measure', 'value')
```
## string
```{python}
df = pd.DataFrame({'text': ['abc', 'DDD','1243c','aeEe'], 'num': [3, 4,7,8]})
df
```
### upper case
```{python}
df>> mutate(text_new=_.text.str.upper())
```
### lower case
```{python}
df>> mutate(text_new=_.text.str.lower())
```
### match
```{python}
df>> mutate(text_new1=if_else(_.text== "abc",'T','F')
,text_new2=if_else(_.text.str.startswith("a"),'T','F')
,text_new3=if_else(_.text.str.endswith("c"),'T','F')
,text_new4=if_else(_.text.str.contains("4"),'T','F')
)
```
### concatenation
```{python}
df>> mutate(text_new1=_.text+' is '+_.text
)
```
### replace
Use .str.replace(..., regex=True) with regular expressions to replace patterns in strings.
For example, the code below uses "p.", where . is called a wildcard–which matches any character.
```{python}
df>> mutate(text_new1=_.text.str.replace("a.", "XX", regex=True)
)
```
### extract
Use str.extract() with a regular expression to pull out a matching piece of text.
For example the regular expression “^(.*) ” contains the following pieces:
- a matches the literal letter “a”
- .* has a . which matches anything, and * which modifies it to apply 0 or more times.
```{python}
df>> mutate(text_new1=_.text.str.extract("a(.*)")
,text_new2=_.text.str.extract("(.*)c")
)
```
## date
```{python}
df_dates = pd.DataFrame({
"dates": pd.to_datetime(["2021-01-02", "2021-02-03"]),
"raw": ["2023-04-05 06:07:08", "2024-05-06 07:08:09"],
})
df_dates
```
```{python}
from datetime import datetime
df_date=df_dates>>mutate(month=_.dates.dt.month_name()
,date_format_raw = call(pd.to_datetime, _.raw)
,date_format_raw_year=_.date_format_raw.dt.year
)
df_date
```
```{python}
df_date.info()
```
## using siuba with database
### set up a sqlite database, with an mtcars table.
```{python}
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from siuba.sql import LazyTbl
from siuba import _, group_by, summarize, show_query, collect
from siuba.data import mtcars
# copy in to sqlite, using the pandas .to_sql() method
engine = create_engine("sqlite:///:memory:")
mtcars.to_sql("mtcars", engine, if_exists = "replace")
```
### create table
```{python}
# Create a lazy SQL DataFrame
tbl_mtcars = LazyTbl(engine, "mtcars")
tbl_mtcars
```
### create query
```{python}
# connect with siuba
tbl_query = (tbl_mtcars
>> group_by(_.mpg)
>> summarize(avg_hp = _.hp.mean())
)
tbl_query
```
### show query
```{python}
tbl_query >> show_query()
```
### Collect to DataFrame
because lazy expressions,the collect function is actually running the sql.
```{python}
data=tbl_query >> collect()
print(data)
```
## reference:
https://siuba.org/